Understanding Progesterone Levels During the First Trimester
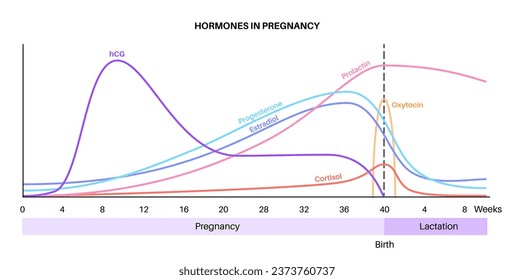
Progesterone plays a crucial role in pregnancy, especially during the first trimester. Monitoring progesterone levels can provide valuable insights into the health of a pregnancy and help prevent complications. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding progesterone levels during this critical period.
What is Progesterone?
Progesterone is a hormone primarily produced in the ovaries by the corpus luteum after ovulation. Its production is later taken over by the placenta as pregnancy progresses. Progesterone is essential for several reasons:
- Preparing the Uterus: It thickens the uterine lining to create a nourishing environment for a fertilized egg.
- Supporting Early Pregnancy: It maintains the uterine lining throughout pregnancy.
- Creating the Mucus Plug: It forms a barrier in the cervix to protect against infections.
- Regulating Body Temperature: Progesterone helps raise basal body temperature, indicating ovulation and pregnancy.
Progesterone Levels During the First Trimester
Progesterone levels increase significantly during the first trimester. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Weeks 1-2: Levels range from 1 to 1.5 ng/ml, right after conception.
- Weeks 2-4: Levels rise to between 2 and 28 ng/ml.
- End of First Trimester: Levels continue to increase, reaching between 9 and 47 ng/ml.
During the second trimester, progesterone levels range from 17 to 147 ng/ml, and in the third trimester, they can reach between 55 and 200 ng/ml.
Also read: Coping With Stillbirth: A Guide To Healing
Why Monitor Progesterone Levels?
Monitoring progesterone levels is crucial for early pregnancy health. Low levels can indicate a threatened miscarriage, prompting further testing and potential interventions to support the pregnancy.
Signs of Low Progesterone
Symptoms of low progesterone include:
- Spotting or Bleeding: Any bleeding during early pregnancy should be reported to a healthcare provider.
- Abdominal Pain or Cramping: Persistent cramping can signal low progesterone levels.
- Frequent Miscarriages: History of miscarriages may warrant monitoring of progesterone levels.
Managing Low Progesterone Levels
If low progesterone levels are detected, healthcare providers may recommend:
- Progesterone Supplements: These can help support the pregnancy.
- Frequent Monitoring: Regular blood tests to track hormone levels.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Stress reduction and rest can help maintain healthy hormone levels.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a vital hormone for maintaining a healthy pregnancy, especially during the first trimester. Understanding and monitoring your progesterone levels can help ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy journey. If you have concerns about your progesterone levels, it’s essential to discuss them with your healthcare provider for the best possible care.
Also read: Understanding Forceps Delivery: What You Need To Know






